Ethiopia’s Health Transformation: Lessons from 30 Years of Partnership
story
JSI’s work in Ethiopia began 30 years ago, with a grant to strengthen reproductive, maternal, newborn, and child health care (RMNCH) services. Since, a deep, trusted partnership with the Ministry of Health, partners, and local organizations evolved and produced gains in almost every area of the health sector from primary health care to a complete digitization of the health sector. As our portfolio grew, we collaborated to address the country’s priorities, ultimately ushering in a health system transformation that provides critical lessons on how health care services can be sustainably strengthened, beyond Ethiopia.
Over the past three decades, through more than 65 projects, JSI has contributed to improving the health outcomes of over 70 million people in Ethiopia.
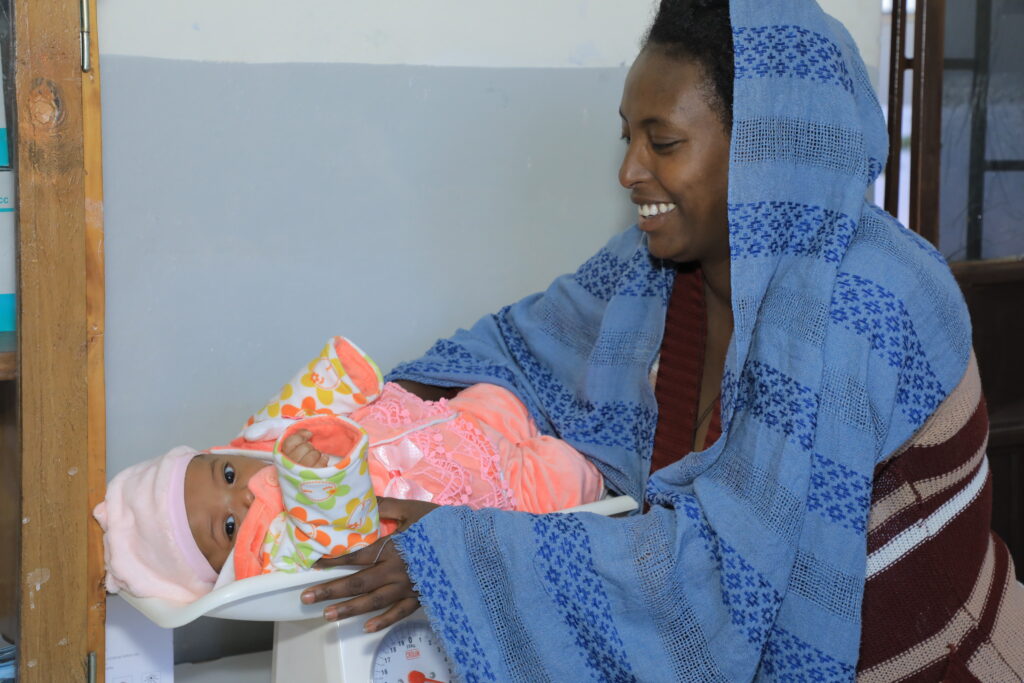

Over the past 40 years, Ethiopia has made RMNCH a national priority—expanding access to essential services, deploying a vast health extension workforce (40,000 frontline community workers that each serve the primary health needs of about 500 households), and implementing targeted policies that reduced maternal and child mortality. Working in-hand with the Ministry of Health, we strengthened infrastructure of long-underserved pastoralist and agrarian health settings and reinforced skills of a growing health workforce. Alongside community leaders, we deployed new cadres, like village health leaders, and approaches like Networks of Care, which tie community dialogue and participation into health program reform.
Over the last 10 years, JSI has helped over 54 million people access RMNCH care, averting more than 85,000 maternal deaths and saving nearly 900,000 infants.
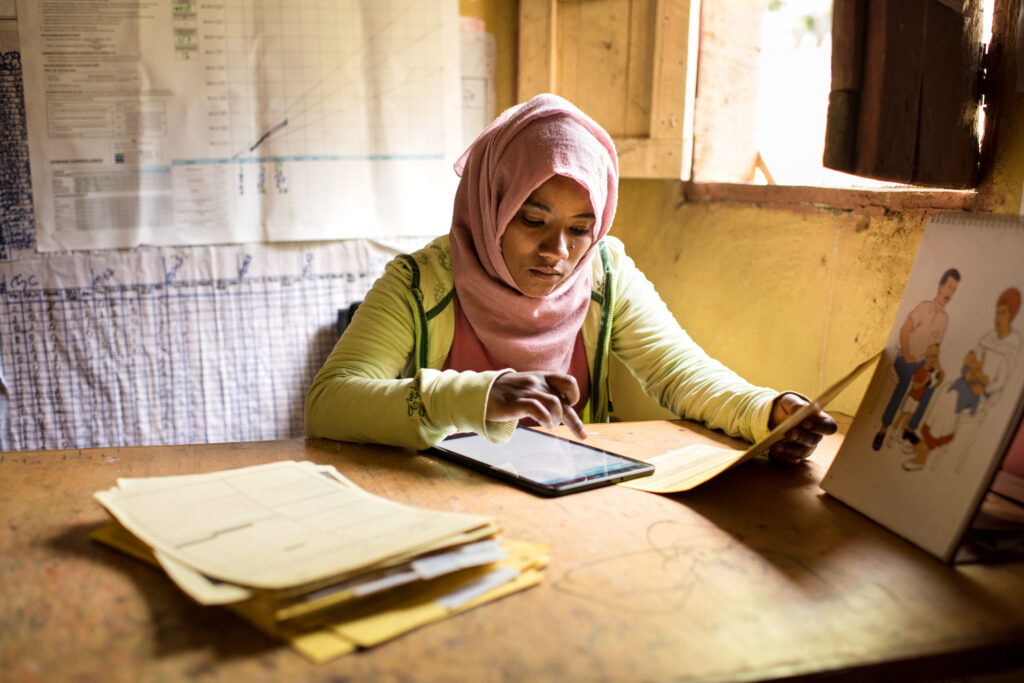

Using our experience and expertise in developing global goods and building interoperable systems, we expanded digital architecture, governance frameworks, and digital solutions. The technology enables the health system to build autonomy and accuracy in routine health data reporting, skills-building opportunities for health workers, and supply chain. We worked with the Ministry of Health to introduce or adapt national systems that collect and use health data, enable secure electronic medical records, and result in better health commodity management. We’ve expanded use of the electronic community health information system, improving data accuracy while easing burdens often placed on frontline health workers. Today, a growing health information technology workforce is managing increasingly robust, real-time data from primary health facilities, while the national supply chain benefits from an end-to-end digital logistics system that cuts costs and reduces stockouts.
New electronic medical records in major health centers resulted in a 11% reduction in mortality. New logistics tools improved product availability by 15%, cut stockouts by 31%, and reduced waste by 8%.
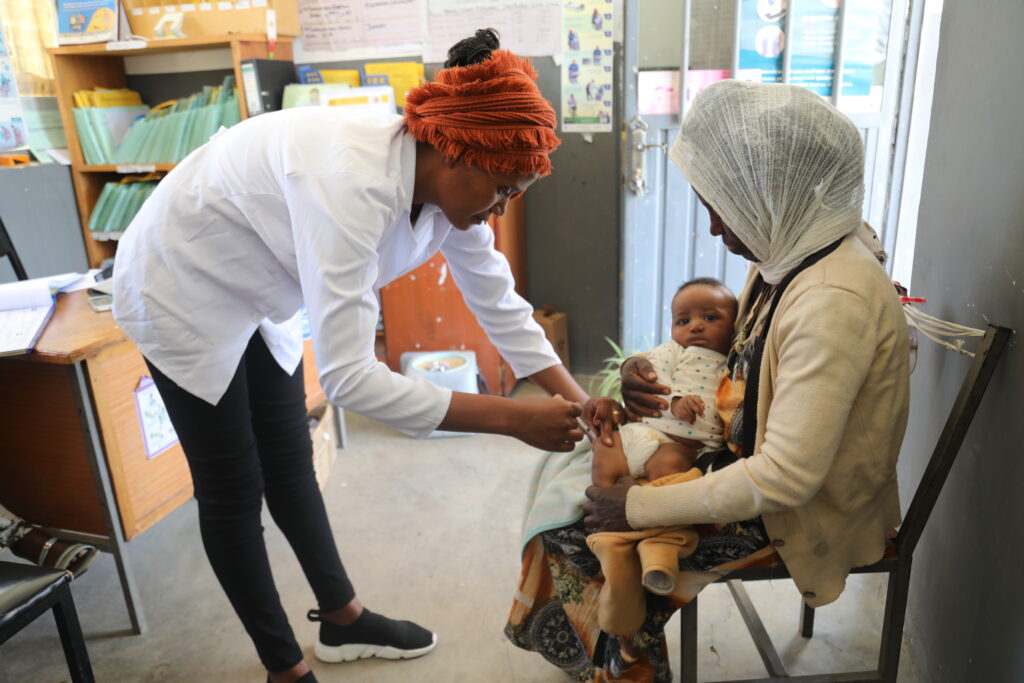
JSI has partnered with the Ministry of Health to reach zero-dose children, training health workers, expanding vaccine coverage, strengthening cold-chain equipment and supply chain management, digitalizing recording and reporting tools, and supporting adoption of national policies. The country’s Expanded Program on Immunization has grown from six to 13 antigens since 1980, with plans for further vaccine introductions, where JSI contributed during planning and rollout of these new vaccine introductions. These experiences demonstrate that long-term investments, strong partnerships, and adaptive delivery models incur positive results, and the same principles can be applied anywhere to strengthen immunization systems and protect communities worldwide.
From 2000 to 2024, Ethiopia made substantial progress in vaccination coverage, with Penta1 increasing from 44% to 81%, Penta3 from 32% to 73%, and MCV1 from 29% to 72%. However, Ethiopia remains the fifth-largest contributor to the global population of zero-dose children, with over 1 million still unvaccinated.
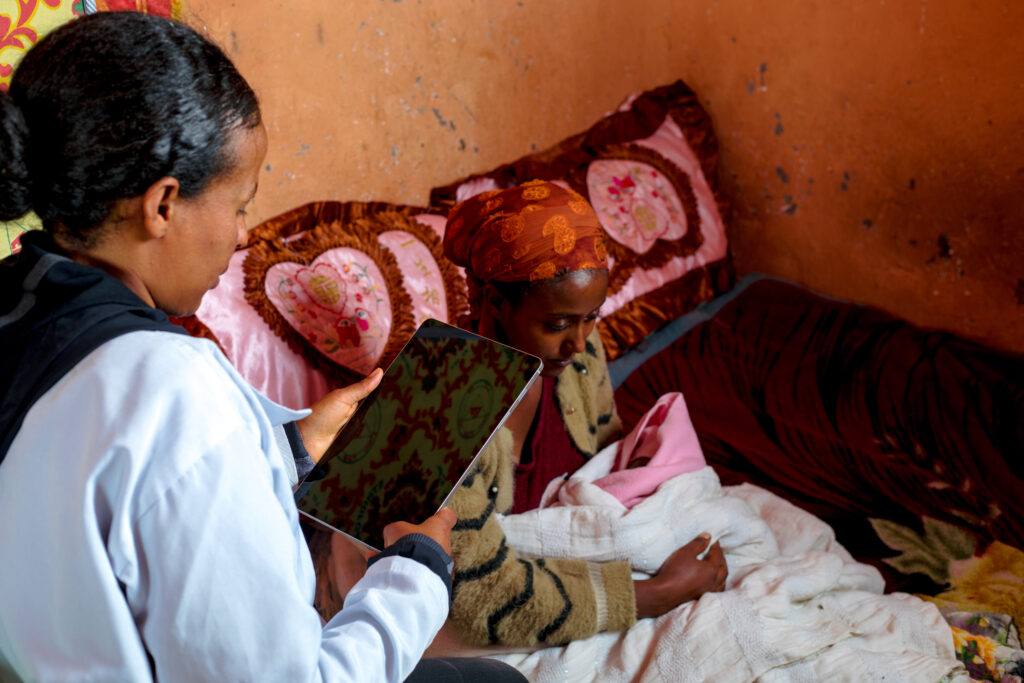

Our localization efforts go beyond government engagement, extending to deep coordination with academic institutions, private sector actors, and grassroots community groups. This collaboration has created a foundation for continuous evidence generation, enabling rigorous research, real-time monitoring, and rapid program adjustments that keep innovations effective and relevant. JSI embeds implementation research into nearly all program activities, allowing innovations to be tested in real time to strengthen current programs and shape future public health approaches.
Our evaluation of an AI diagnostic tool within eCHIS found that it detected abnormalities in over 30% of malaria RDTs. This suggests AI could be used as a powerful quality-control mechanism for improving diagnosis, treatment, and supply chain monitoring.
At the heart of JSI’s work in Ethiopia is a commitment to adaptive learning, co-designing solutions with our partners, implementing innovations at scale, and driving lasting local solutions. Over the past thirty years, these approaches have helped strengthen primary health care, with a focus on service quality and community mobilization, and laid the groundwork for the successful integration of supply chain management, health systems strengthening, and digital health innovations. This evolution has contributed to improved health outcomes for women, children, newborns, and adolescents, while reinforcing Ethiopia’s vision of health care for all. The country’s commitment—together with the dedication of its partners—has created a health care landscape that offers these lessons. The journey continues, with innovation and continuous improvement at the center of advancing health system performance.
We strive to build lasting relationships to produce better health and education outcomes for all.